Introduction
There has been an explosion of interest – and concern – around the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in healthcare delivery. The safety and effectiveness of leveraging these technologies really come down to the specific use case.
Patients want the assurance and trust that comes with a qualified and experienced physician directing their care – not a chatbot. A recent Pew Research survey of U.S. adults found about eight-in-ten (79%) would not want to use an AI chatbot if they were seeking mental health support.
Physicians wanting to use their knowledge, skills and experience in care delivery don’t want to contend with technology coming between them and their patients. However, in a recent Medscape survey of U.S. physicians, over half (56%) described some level of enthusiasm about AI offering diagnosis and treatment options to supplement their recommendations.
Instead of developing AI/ML applications that try to replace the physician in patient interactions or insert barriers between the parties, the most advantageous approach is to employ these technologies to support physicians during episodes of care. Positioning the power of AI/ML to analyze vast volumes of data and surface insights behind the physician while they are facing the patient preserves the value of the personal connection between physician and patient.
The full white paper explores use of AI/ML in a virtual environment using a physician-first care and guidance model to empower physicians with real-time information during an episode of care. Improving efficiency in care interactions by surfacing valuable insights to the physician for their evaluation and potential use – as opposed to them having to search for information – supports the delivery of higher quality care to a greater number of patients at a lower cost.
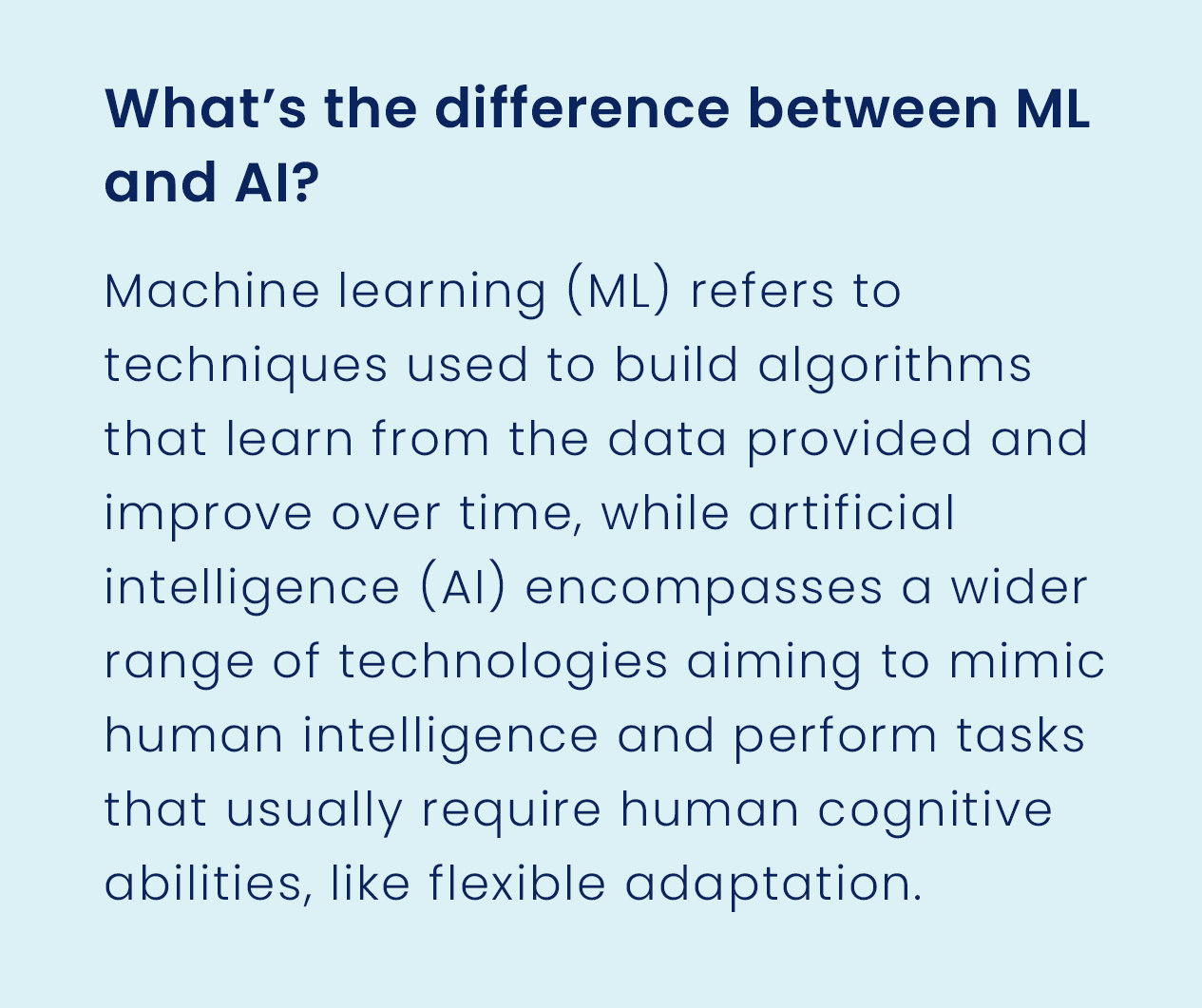
What challenges are surfacing with deployment of new AI/ML-based services in healthcare?
While AI and ML have the potential to support clinical care delivery, some applications to date, most notably those that have attempted to put the technology in the place of a physician or between the physician and patient, have revealed the dangers of this approach. Read the full white paper to learn more about:
- Conflicting advice to cancer patients
- Dangers of drug misinformation
- Ethical issues in behavioral health
- Inaccurate and incomplete data sets

What are some of the opportunities to use AI/ML — effectively — in patient care?
CirrusMD is now leveraging its vast quantity of accurate and complete data for AI/ML enabled intelligence, where the technology doesn’t replace the physician or come between the physician and patient, but instead, surfaces valuable insights for physicians to consider during patient chat encounters.
Read the full white paper to learn more about:
- Surfacing insights and resources to physicians
- Navigation to health benefit specific resources
- Coding and billing efficiencies that reduce physician work

How is CirrusMD using AI/ML to support physicians and improve care delivery?
CirrusMD understands how AI and ML can be used as highly effective tools to accelerate physician workflows and deliver more customized care to their patients - and not to replace an actual doctor.
By “listening” to both patient and provider messages during a care encounter, CirrusMD’s AI/ML tools can see the full picture and focus on improving the situation rather than trying to emulate a doctor. The result is an uninterrupted dialogue between patient and doctor where AI/ML serves as an assistant, allowing doctors to remain focused on caring for the patient.
Conclusion
The surge of interest and apprehension surrounding the integration of AI and ML in healthcare necessitates a nuanced approach. Striking a balance is imperative to address concerns and capitalize on the potential benefits offered by AI/ML. Rather than displacing or creating barriers in physician-patient interactions, the most advantageous strategy involves deploying AI/ML to support physicians during episodes of care. With a collaborative approach, not only is better-informed decision-making facilitated, but there are also new opportunities to deliver higher quality care to a larger patient population at a reduced cost, showcasing the transformative impact of thou ghtfully integrating AI/ML into healthcare practices.





